SUBTALAR OVERPRONATION
The foot provides mechanical stability for the entire body when standing, walking, jumping, and running, The foot and it's internal elements such as: bones, ligaments, tendons, provide initial shock absorption for the entire body. The foot and all of its structures adapt accordingly to the weight bearing demands placed upon it. The subtalr bone is positioned between the Tibia and Fibula of the lower leg. The Subtalr joint is crucial for the flexion and extension of the foot. The joint is supported by several key ligament structures. Subtalar overpronation occurs when one or several of these supported structures is weakened due to injury or overuse.
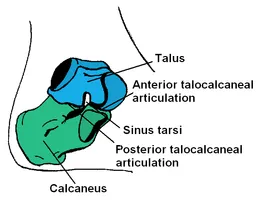
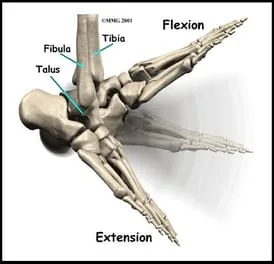
MECHANICS OF THE SUBTALAR JOINT
The Talus or Talar bone articulates with the Tibia, Fibula, Calcaneus (heel bone). During a normal Gait (walking) cycle, the following occurs: the Calcaneus (heel) tilts to the outside, the talus moves upward and to the inside, the tibia totates to the inside while the knee flexes. Subtalar joint pronation is normal during walking and running, it is necessary to absorb the force of the heel striking the ground.

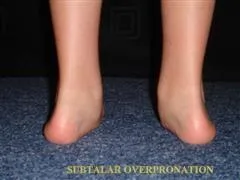
CAUSES OF SUBTALAR OVERPRONATION
There are many causes of Subtalar overpronation, perhaps the most common is long distance running. Excessive stress on the plantar fascia (sole of foot), causes weakening of the supporting structures, leading to abnormal stress of the articulations of the Subtalar Joint. The ligaments supporting these structures weaken over time causing a decrease in the shorck absorption capability of the foot. Over time this weakening is felt in the shins, knees hips, lower back, and throughout the spine.
A tight Achilles tendon caused by overuse, inactivity,pregnancy,sports injury, etc., stresses the calcaneus in an upward position, causing the Subtalar Joint to overcompensate, leading to further injury.
Muscular spasms of the Gastrocnemius (calf muscle), Peroneal Longis, Peroneal Brevis (muscles of the lateral leg), causing a flat foot. Overuse and without stretching these muscles causes abnormal amounts of subtalar pronation leading to a weakening of the supporting structures.
TREATMENT
First and foremost, it is imperative to correct the alignment of the foot and support the arches in a neutral biomechanical position. Most patients are fitted for
ORTHOTICS
, helping to stabilize the feet in the neutral position, reduce stress on the ligaments, bones, muscles.
ORTHOTICS
along with Massage Therapy, Chiropractic adjustments, stretching, ice, and re-education, are the most effective modes of treatment of this condition, and aid in prevention of further injury.